Two Stage Beer Wort Plate Heat Exchanger Price For Brewery
Plate heat exchanger. All sizes can be delivered with one or two stages.
The model with one stage is primarily designed for cooling with tap water.
The model with two stages are cooling with tap water in one zone and glycol from cooling system in the other zone.
Heated tap water can be reused for brewing. Different size depending on demand.
$2,999.00 $3,500.00
Heat transfer is the core function of a heat exchanger. The laws of thermodynamics provide the basic rules for heat-exchanger design:
1st Law of Thermodynamics: A heat exchanger cannot destroy or create energy, but there is always a balance between the hot and cold sides.
2nd Law of Thermodynamics: Heat flows from a hot medium to a cold medium to equalise the temperature difference.
Heat transfer is the exchange of heat between hot and cold bodies. There are three fundamental modes by which this occurs:
- Conduction
- Radiation
- Convection
Heat transfer in a heat exchanger is a combination of conduction and convection. Conduction and convection are calculated in each heat-transfer case.
Calculating heat transfer
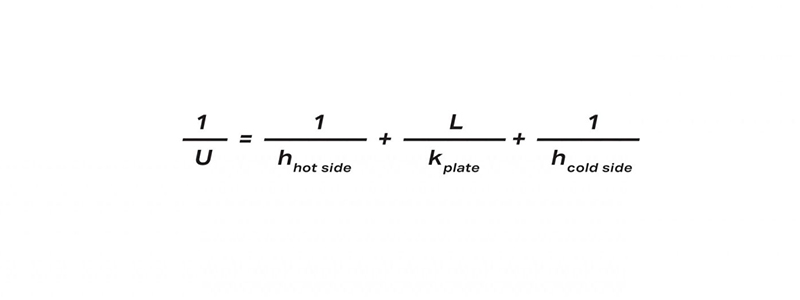

The total heat-transfer coefficient U is calculated by the sum of the convective heat transfer from both sides (hhot and hcold) of the heat-transfer surface and conduction (k) through the heat-transfer plate.
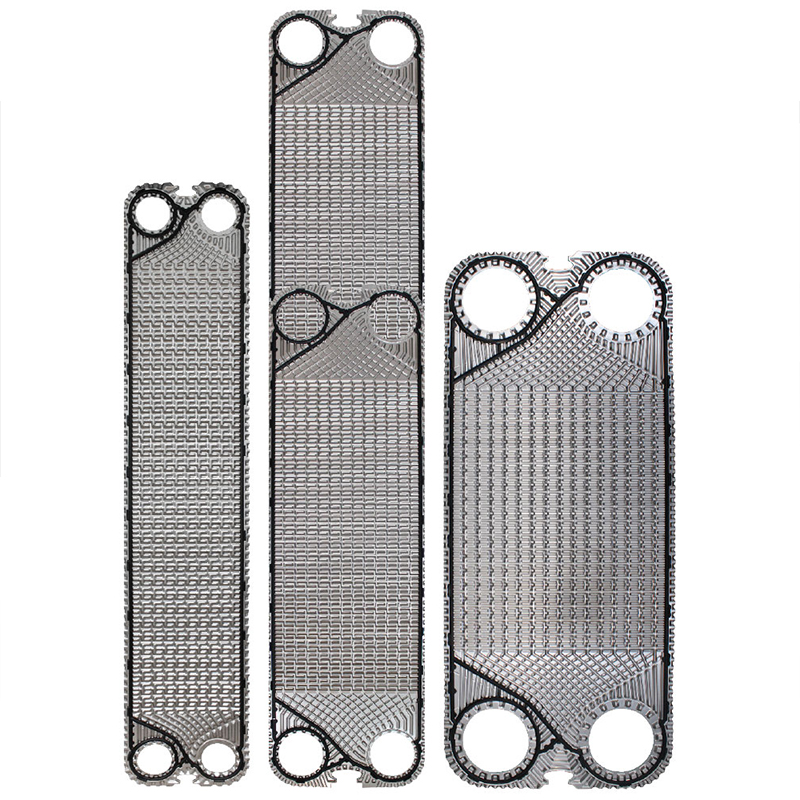


Description
- High efficiency plate frame heat exchanger
- Sanitary grade
- Stage: Single or Double as preferred
- Tri clamp connection
- EPDM gasket
- With thermometer for checking wort temp
- With aeration unit for oxygenation.
- Including: wort inlet/outlet, cold water inlet/outlet temp, flow rate etc
- The second stage is an option, in case customer use glycol for cooling.
- Triclamp connection
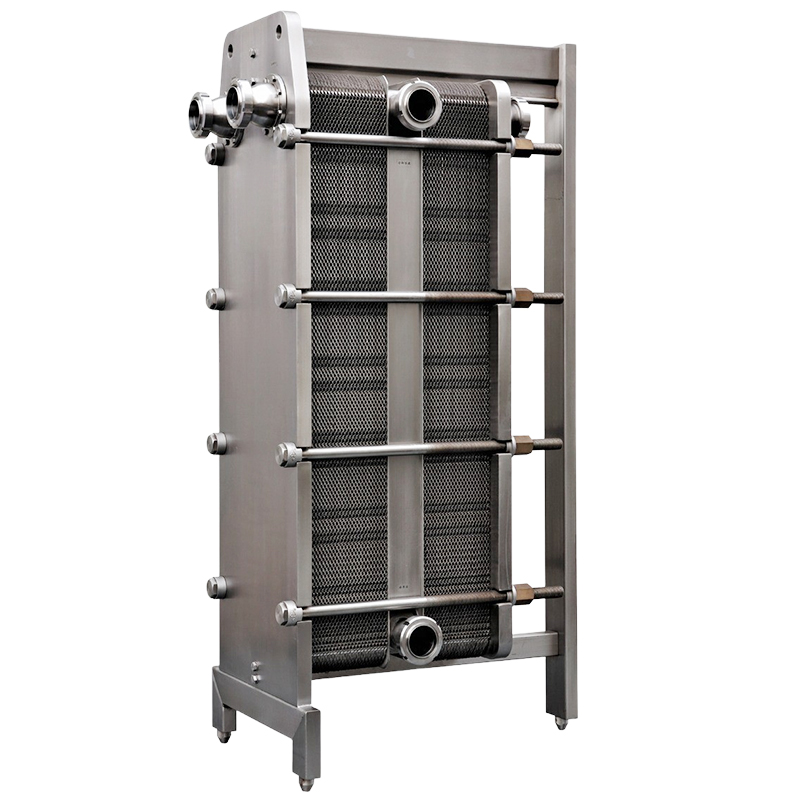
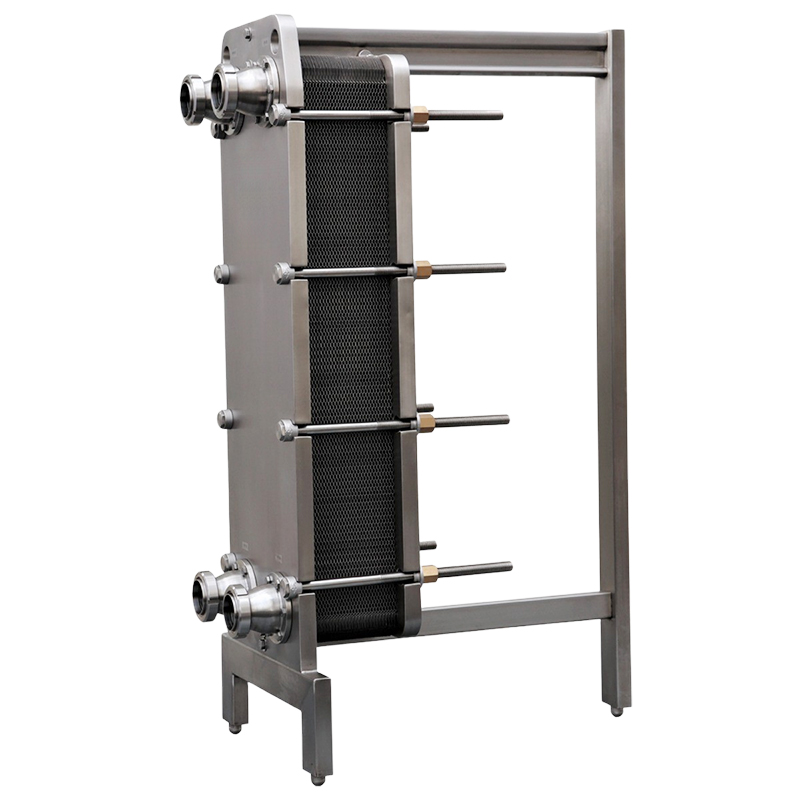




| Model | Capacity L/H | Max piping connection |
| 2M2 | 300 | 32mm |
| 3M2 | 500 | 32mm |
| 4M2 | 600 | – |
| 5M2 | 830 | – |
| 6M2 | 1,000 | 38mm |
| 8M2 | 1,300 | 38mm |
| 10M2 | 1,600 | 51mm |
| 12M2 | 2,000 | 51mm |
| 15M2 | 2,500 | 51mm |
| 18M2 | 3,000 | 51mm |
| 20M2 | 4,000 | 63mm |
| 25M2 | 5,500 | 63mm |
| 30M2 | 7,000 | 76mm |
| 40M2 | 8,000 | – |





