Stainless Steel Plate Heat Exchanger PHE
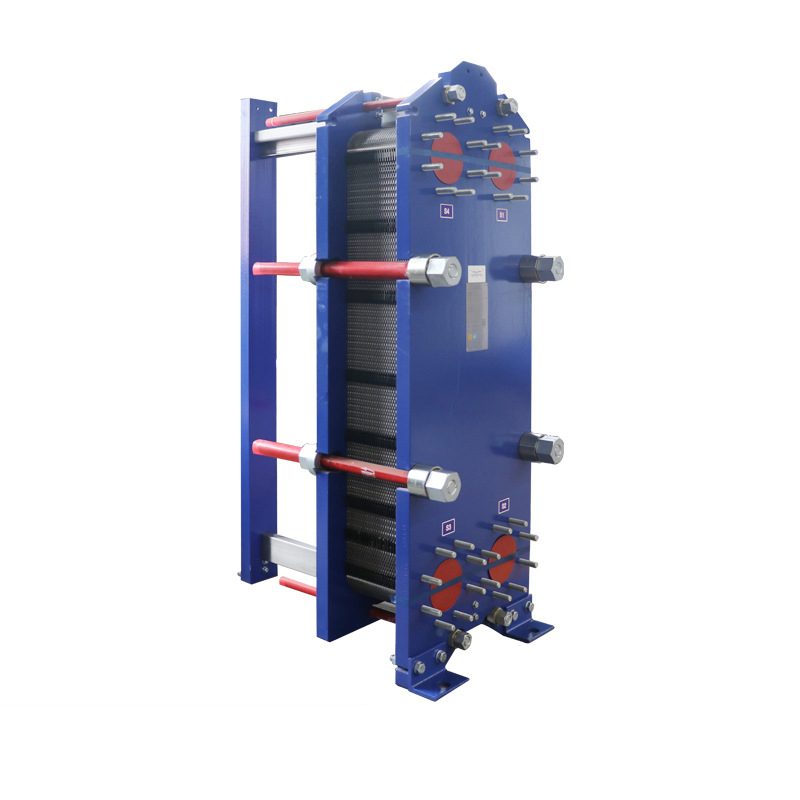
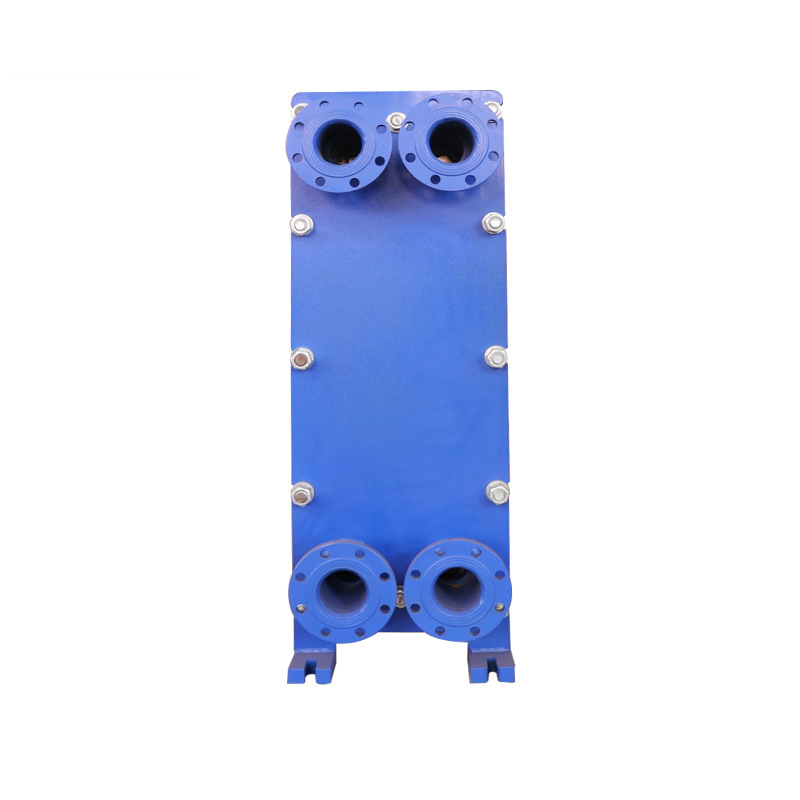
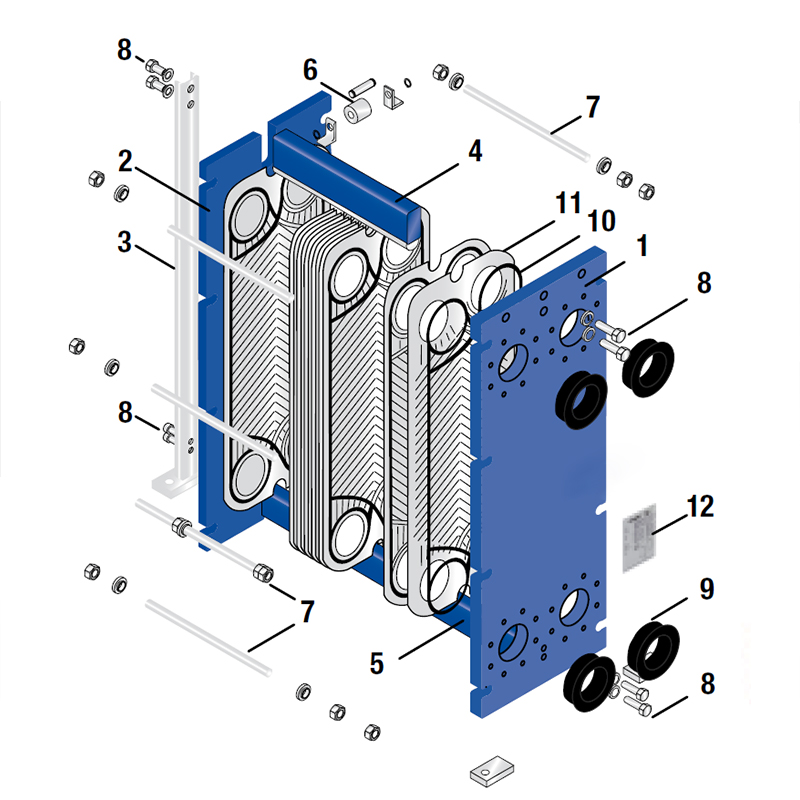
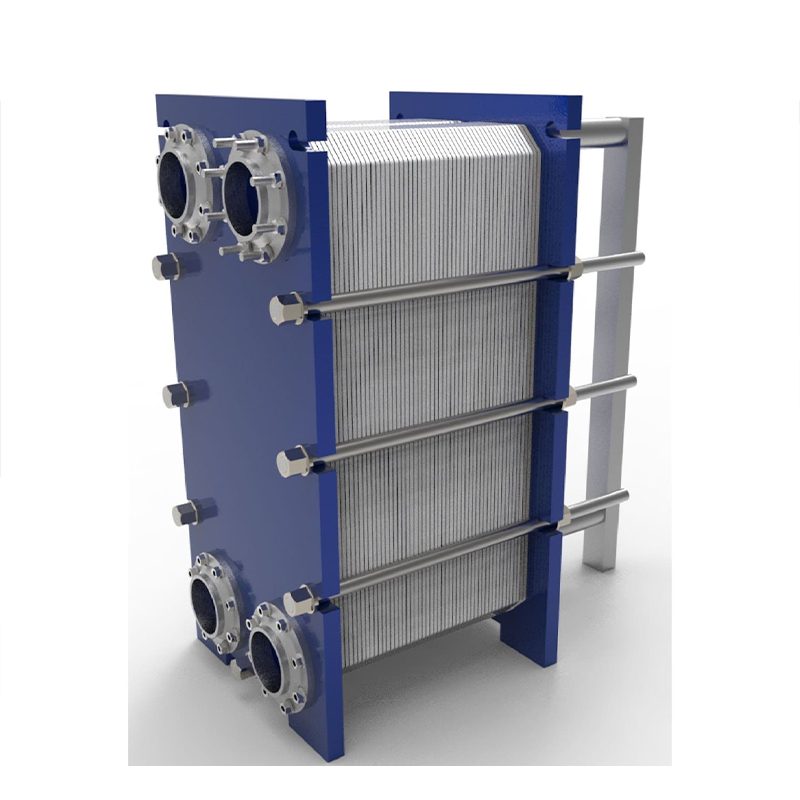
The plate heat exchanger is a detachable heat exchange equipment composed of many corrugated heat transfer plates and rubber gaskets. The heat transfer plates are arranged at certain intervals, and then pressed with rubber gaskets to form a plate heat exchanger.
When the plates are assembled, the two groups are arranged alternately, and the plates are fixed with rubber sealing strips. The function is to prevent fluid leakage and form a narrow net-shaped flow channel between the two plates.
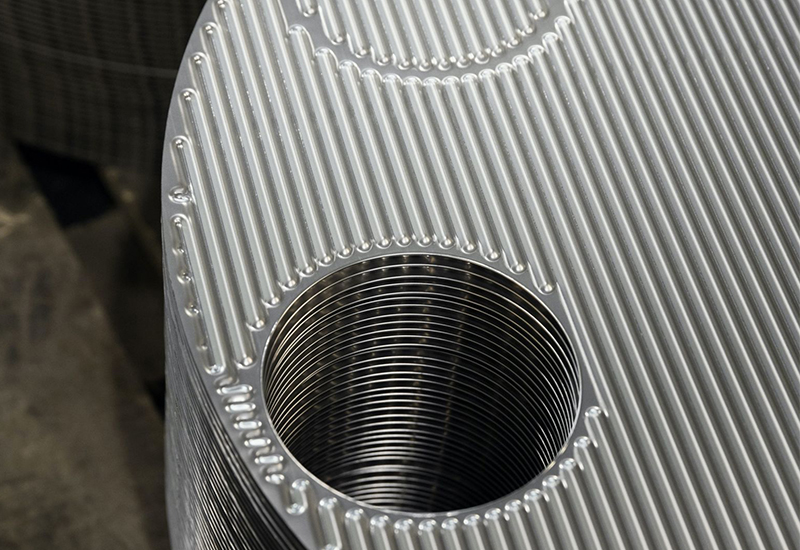
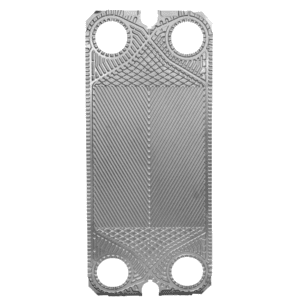
The heat exchange plates are pressed into various corrugated shapes to increase the area and rigidity of the heat exchange plates, and to enable the fluid to form turbulent flow at low flow rates to enhance heat transfer.
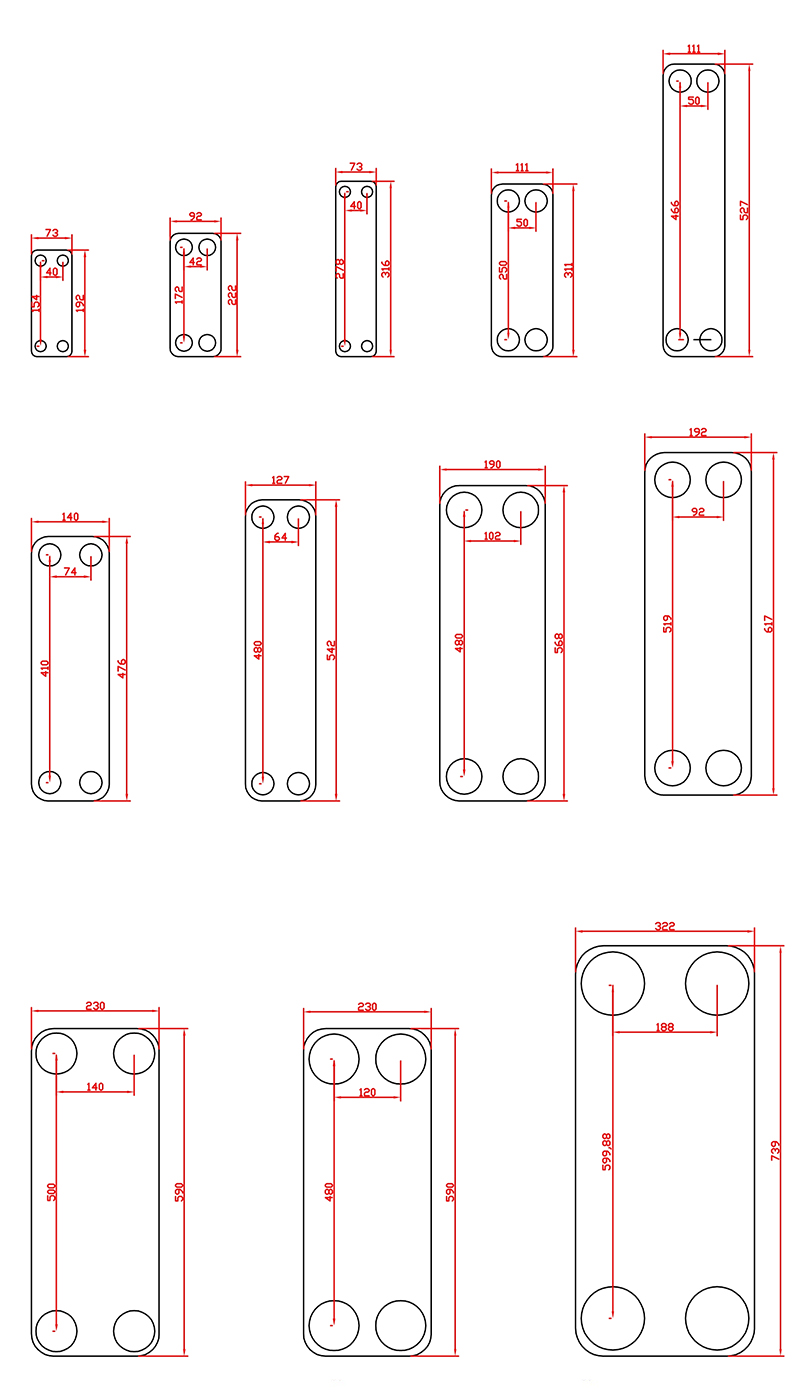
The four corner holes on the heat exchange plates are the distribution pipes and drain manifold of the fluid. The two heat exchange media flow into their respective flow channels to form countercurrents, and heat is exchanged through each plate.
$2,500.00 $3,000.00
The Principle of a Plate Heat Exchanger
The PHE device makes use of the principle of thermodynamics. In these exchangers, each plate has a confined, concave tubular shell. The plates are arranged in such a way that thin channels that are rectangular in shape are developed to change heat through partial pieces.
Between these twisted and narrow channels, the operating fluid flows. The plates of this exchanger are girdled by gaskets to control the fluid flux. These gaskets are arranged in such a way that only one type of liquid (like a canvas which is being toasted) distributes on one plate, and another fluid (like hot water) distributes on the coming plate.
After this arrangement, the cold and hot fluids alternatively suffer the plate, whereby a heat exchange takes place. The plates have a large face area; thus, they offer an excellent heat transfer rate than tubular heat exchangers.




Advantages of plate heat exchangers
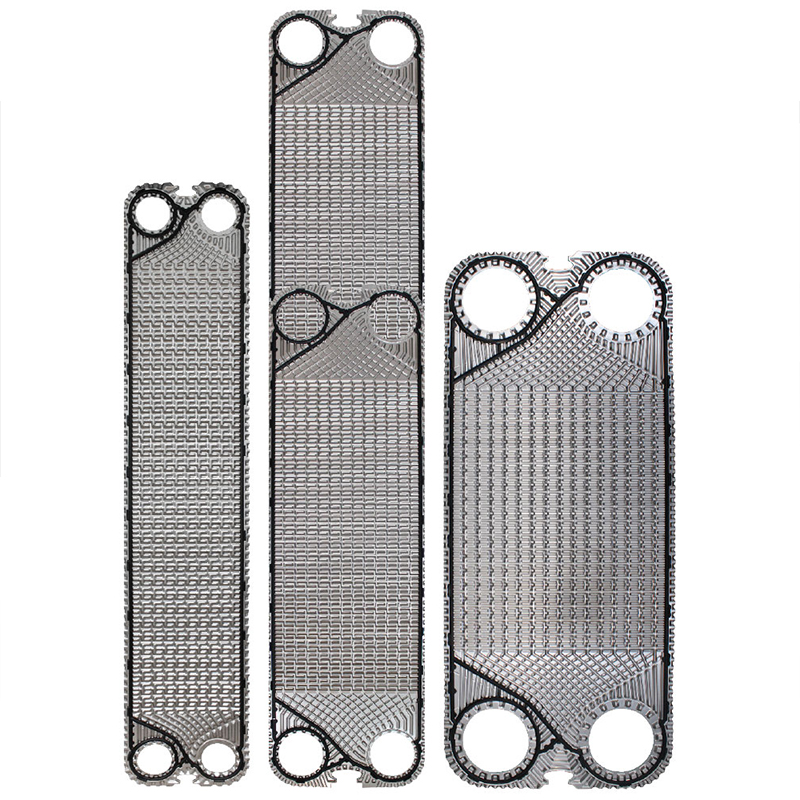
- The inlet shunt area of the heat exchange plate is designed with a streamlined guide groove, which has the effect of narrowing the difference in flow resistance on different flow channels.
- It makes the fluid evenly distributed in the plate heat exchange area, thus avoiding the disadvantages of heat exchange efficiency decrease, pitting corrosion and scaling caused by uneven flow distribution and flow dead angle.
- For the plate with a larger width, the equalizing groove along the equipotential line is also added, so that the streamline guide groove and the equalizing pressure groove along the equipotential line intersect to form a grid-like inlet shunt area with little resistance. The grid-shaped inlet distribution area has a perfect flow equalization effect.
- At the same time, the shunt area also plays a role in rapidly forming turbulent flow to carry out strong heat exchange.
- Participate in heat exchange in advance through the diversion area, which effectively increases the heat exchange length and reduces the heat exchange area.







Partially Sealed Heat Sink Material Notes
| Material | Temperature Range | Applicable Media |
| EPDM rubber (E) | -50℃ – 150℃ | Water, general organic and inorganic acids, alkalis and chemical media |
| Nitrile rubber (N) | -20℃ – 110℃ | Water, oil, aldehyde and general corrosive medium |
| Food and medical rubber (S) | -20℃ – 120℃ | Food materials, materials for the pharmaceutical industry |
| Fluororubber (F) | 0℃ – 180℃ | Organic solvents, acids, bases, alcohols, oils |
| Neoprene (C) | -40℃ – 100℃ | Alkali and some acids |
| Silicone Rubber (Q) | -65℃ – 230℃ | Some oils, alcohol |




There are no reviews yet.