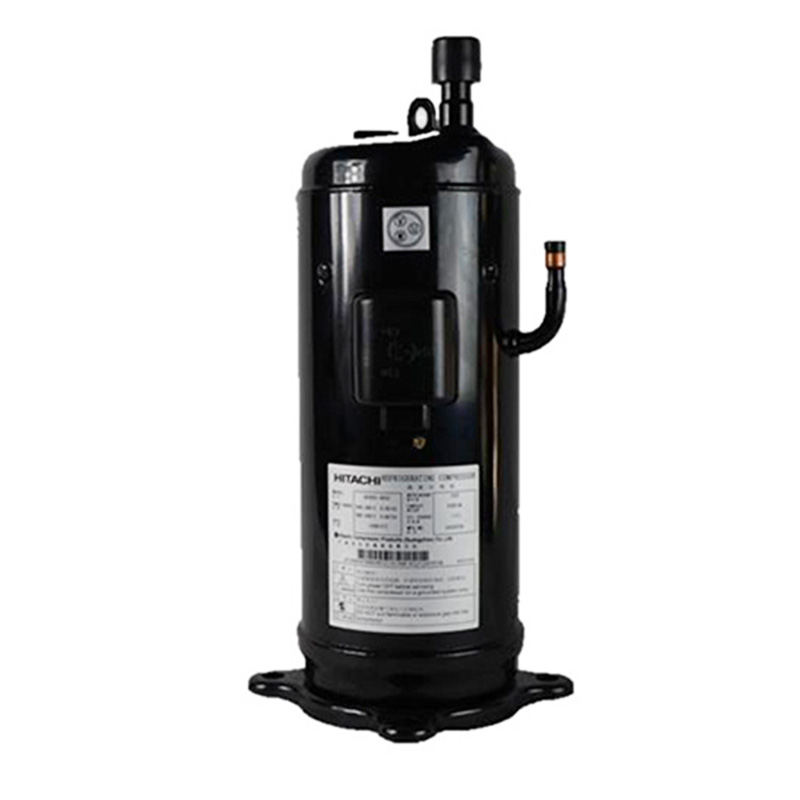
5HP Fixed Frequency Hitachi Air Conditioning Compressor G503DH-80D2
The air conditioner compressor plays the role of compressing and driving refrigerant in the air conditioner refrigerant circuit. The air conditioner compressor is generally installed in the outdoor unit. The air conditioner compressor extracts the refrigerant from the low-pressure area, compresses it, and then sends it to the high-pressure area for cooling and condensation
$390.00
CompareCompressor Definition
The air conditioner compressor plays the role of compressing and driving refrigerant in the air conditioner refrigerant circuit. The air conditioner compressor is generally installed in the outdoor unit. The air conditioner compressor extracts the refrigerant from the low-pressure area, compresses it, and then sends it to the high-pressure area for cooling and condensation. The heat is released into the air through the heat sink, and the refrigerant also changes from gaseous to liquid, and the pressure increases.


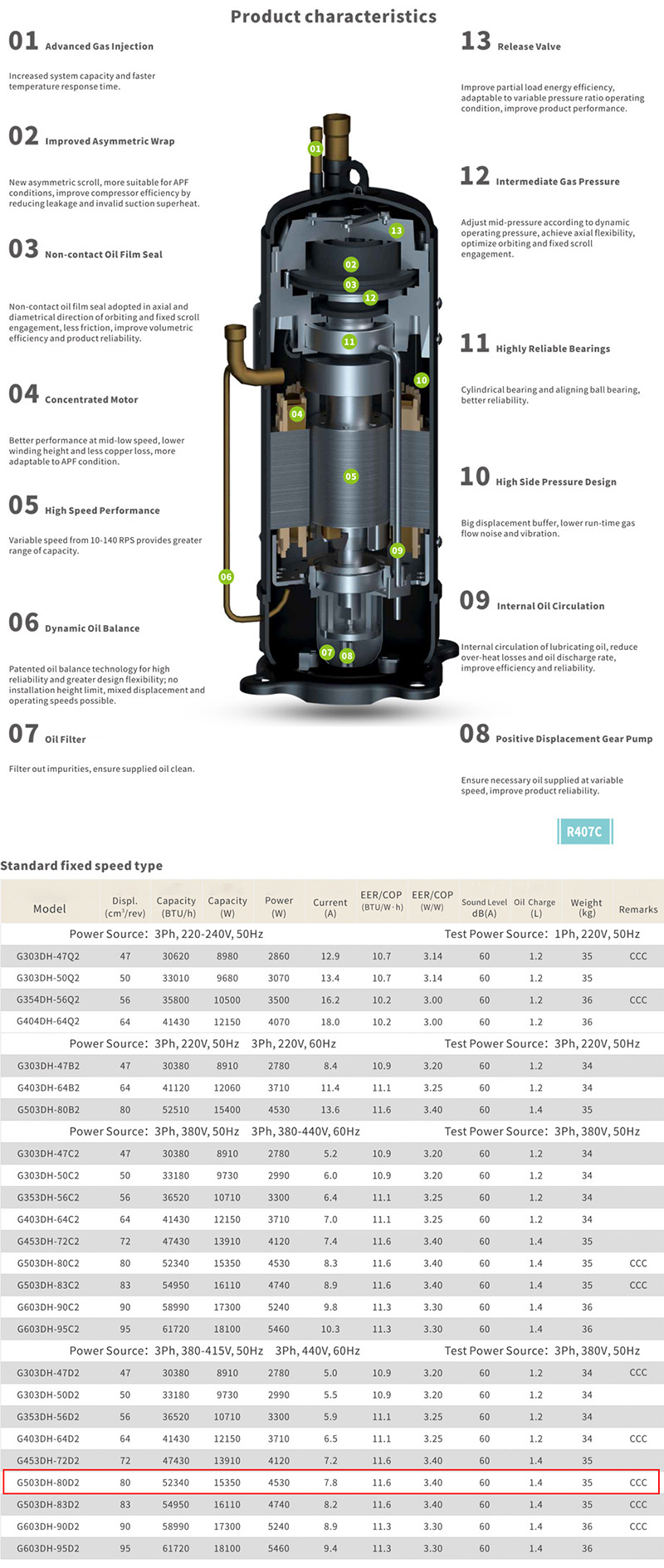

The working circuit of the air conditioner compressor is divided into evaporation zone (low pressure zone) and condensation zone (high pressure zone).
The indoor unit and outdoor unit of the air conditioner belong to the low-voltage or high-pressure area respectively (depending on the working status).
The refrigerant then flows from the high-pressure area to the low-pressure area, and is sprayed into the evaporator through the capillary tube.
The pressure drops suddenly, and the liquid refrigerant immediately becomes gaseous, and absorbs a large amount of heat in the air through the heat sink.
In this way, the air conditioner compressor works continuously, absorbing the heat from one end of the low-pressure zone into the refrigerant and then sending it to the high-pressure zone to radiate into the air, which plays a role in regulating the temperature.





There are no reviews yet.